
The Power of Scheduled Automated Backups for DevOps and SaaS
In 2020, a DevOps team at a mid-sized fintech startup almost lost its entire source code. A failed container update caused a cascading failure in their self-hosted GitLab instance. The backup was… somewhere. No one checked it in weeks. The recovery process took three days. The cost was around $70,000 in downtime and customer compensation.
The event wasn’t a matter of not having a backup strategy. It was a matter of assuming someone, somewhere, had run the proper function at the right time. In this case, no one has.
The case for scheduling. Why manual backups don’t scale
Nowadays, manual backups resemble trying to pull a horse cart onto a Formula 1 track. All the more so in DevOps. In short, they belong to another era.
Development pipelines usually evolve hourly. New repos are spun up during sprints. Secrets rotate and workflows change. No matter how much caffeine you provide, even the most focused engineer can’t match or keep up with the constant, often rapid changes in the DevOps environment.
New repositories, updated pipelines, rotated secrets, and shifting permissions – these changes can occur multiple times a day, often across distributed teams. And so, manual oversight simply can’t scale.
Scheduled, automated backups replace ad-hoc actions with digital discipline. They ensure that source code, metadata, configurations, and secrets are preserved continuously, not retroactively. And it’s not about convenience but rather data and business continuity.
Backup scheduling frameworks allow teams to define frequency, scope, and logic:
- hourly backups of active projects
- daily full backups of the production environment
- weekly compression of dormant repositories.
Such schedulers adapt to business hours or maintenance windows. They reduce system load without sacrificing backup fidelity.
Compression. A thing for backup efficiency
Let’s assume your DevOps platform generates 100 GB of backup data per week. Now, let’s multiply that amount by 52 (weeks in a year) first, then by the number of environments you manage. Having the final number, consider your storage bill.
To reduce such a cost, you use compression. However, it’s not about lowering storage costs alone. The idea is to:
- speed up transmission
- reduce I/O latency
- make restores faster, especially when seconds count.
It’s worth underlining that today’s backup tools (modern ones, as marketing calls them) implement block-level deduplication, delta encoding, and intelligent compression algorithms. The latter also contains a popular wording, but in this case, the mechanism doesn’t just shrink data blindly – it:
- analyzes patterns
- removes redundancy
- stores only what has changed or is essential.
In backup, this means faster transfer and smaller storage footprints. Ultimately, this translates into quicker restores. It’s because the system avoids saving the same blocks of files repeatedly. And that’s a more efficient and context-aware solution. A smart one!
Additionally, these capabilities enable a full weekly backup to function like an incremental one. It also saves on storage space and is fast in transit while being precise in content. So, you get the complete picture instead of a burden.
Time, control, and sanity are your team’s gains
From the performance and control perspective, every engineer who doesn’t verify backups manually is doing something worthwhile. The above may sound like a silly statement, yet scheduled automation reclaims hours that would otherwise be spent clicking through logs or manually archiving repos.
It’s also about clarity. A scheduled system doesn’t forget, doesn’t get sick, distracted, or promoted to another department. It just runs as designed.
Besides, this is not limited to reducing workload only. Such an environment standardizes expectations. During audits, the team knows where to find historical states. Furthermore, in case of an incident response, they can act instead of searching.
Most importantly, automated backups restore a sense of psychological safety. That’s not fluff but operational readiness.
Monitoring and observability. Know when something goes wrong
Scheduling is only the beginning. A backup that silently fails is worse than no backup at all. Effective automated systems integrate monitoring and alerting. It isn’t restricted to “backup succeeded” banners, but provides deep insights:
- skipped objects
- version mismatches
- retention conflicts
- integrity violations and others.
REST APIs enable this telemetry to be fed directly into existing SIEM or platforms (if applicable). Backup health should be visible in the same observability space as deployment metrics and application logs. If you’re watching your pipeline latency, you should also be watching your backup status.
Best practices for backup automation in DevOps and SaaS environments
Considering best practices in backup automation for DevOps, the first principle is scope, which refers to what exactly gets backed up for faster and more reliable data recovery.
The first: scope
The catch here is not just backing up repositories, but also considering backing up metadata. SaaS platforms abstract infrastructure. That doesn’t mean, however, that data is disposable.
In a disaster scenario, restoring a Git repository without its metadata is akin to restoring a WordPress site without its database.
The second: isolation
The second thing about best practices is isolation. All backups should (or must) be stored independently of the source environment. If GitHub, Azure DevOps, Bitbucket, or GitLab goes down, you cannot rely on their API to access your saved states. Such a separation is not paranoia but a well-thought-out protocol. Following it, you can still restore your data when the main platform fails.
Of course, some may react with “duh”, yet reality shows that such a banal fact is not common knowledge. Especially among IT experts, who treat Git-based SaaS services as an ultimate and trustworthy solution.
You aren’t one of them, are you?
The third: policy
The next thing is policy. In this section, define retention rules that align with both compliance and business continuity. Although a thirty-day retention window may satisfy auditors, it may not be sufficient if a misconfiguration corrupted your system six weeks ago.
The fourth: testing
It’s a final but equally necessary element. It’s vital to keep in mind and practice that scheduled backups are as helpful as their restore scenarios. So, schedule not just backups, but the whole drill. The time to discover that your workflow metadata wasn’t included is not after a breach!
Real-world integration. How teams do it right
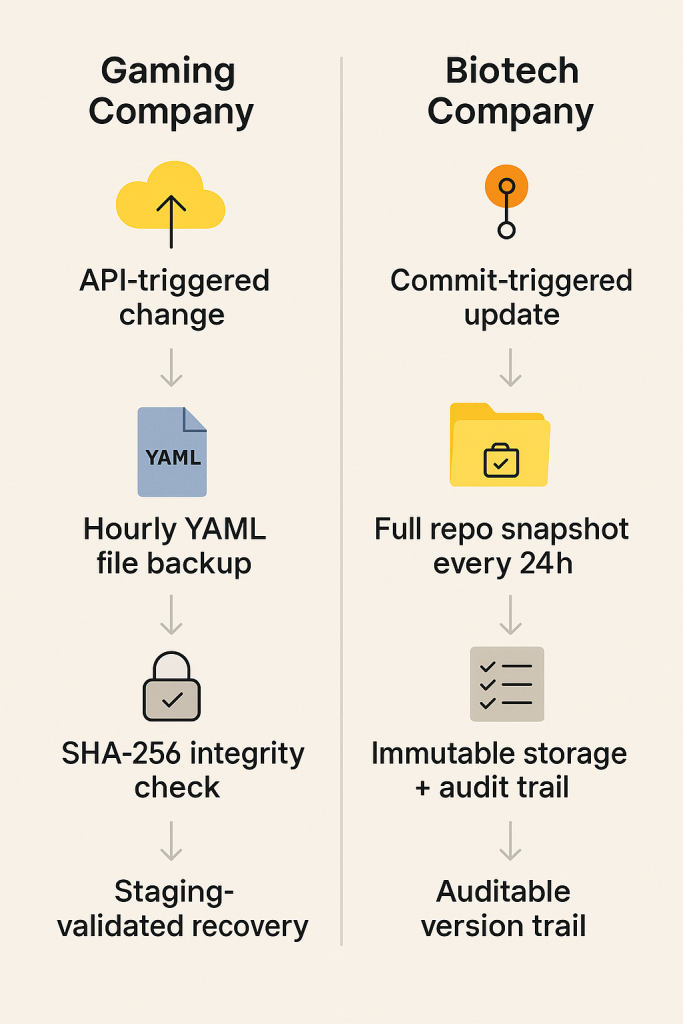
Picture a distributed gaming company. The organization is working with cloud-based GitOps pipelines that face frequent reconfigurations tied to multiple third-party APIs. They scheduled critical YAML files hourly, protected by immutable storage. Every restore here was cross-validated against SHA digests and tested in staging.
Another example may be related to a biotech company. Its regulatory obligations demanded the exact history of repository changes. However, their team didn’t have time to verify manual exports. Automated backups triggered by commit activity ensured that the system captured new objects in real time, while also archiving full snapshots every 24 hours. Zero-touch and fully compliant.
The examples presented in both cases are neither extravagant nor overly complex. They’re a routine, once well-designed automation is in place.
Why schedulers alone aren’t enough
Some things must go beyond scripts. Many teams are leaning on shell scripts to schedule backups via cron. Well, it’s better than nothing, but it’s also a fragile scaffold, including hardcoded paths, no integrity verification, and no centralized monitoring.
In other words, when a script fails silently, no one notices. No one, until they do. That’s why mature solutions:
- integrate with IAM
- offer role-based access
- support granular restore and many more.
It means that whether you need to restore a deleted repository, a specific pull request comment, or an issue thread, it should be easy and quick.
The GitProtect approach
At this point, it’s worth noting that GitProtect – the Backup and Disaster Recovery system – automates backup scheduling with surgical precision. Its policy engine handles frequency, data coverage, storage targets, and retention – all in a UI or via API. The tool compresses, encrypts, and monitors all needed elements of your dataset.
And yes. It integrates with DevOps ecosystems like GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, Azure DevOps, and Jira. The solution allows you to see what’s necessary. Even in case you forget something, you’ll never lose visibility.
There’s something to be said for a system that keeps working long after everyone’s forgotten it’s even running. That’s more or less the point with GitProtect. You don’t just line up the schedule and walk away—it keeps things in check. Locks what’s been saved. Ensures that no one, not even those with admin keys, can tamper with the copies once they’re in place. Not by accident, not by design.
Restoring isn’t boxed in either. If things move from GitHub to GitLab – or back – the backups don’t complain. They follow. The data appears where you need it, in the format you left it.
There’s also a quiet background process that constantly checks the information it stores. Not just counting files or ticking off timestamps. It’s testing whether the backup would work if you had to lean on it. You probably wouldn’t notice unless something’s wrong. That’s the idea.
And when someone does ask for proof, compliance, audit, or legal, you’re not scrambling. Every step’s been logged already. The system isn’t shouting about it, but the record’s there. Like an invisible notebook someone’s been keeping for you.
All in all, it’s not flashy. That’s probably the point. It just doesn’t forget. Even when you do.
👉 Explore more: 11 SaaS Backup Solutions And Tools To Keep Your Data Safe
To sum it up
The whole idea with engaging scheduled automated backups isn’t about convenience. Maybe a bit. The main point here is data, environment, and thus, your company’s resilience. In DevOps and SaaS-driven markets, where downtime is a liability and human errors are a certainty, automation is the baseline, not the bonus.
Whether your goal is compliance, continuity, or simply a good night’s sleep, the true power of scheduled backups lies in their quiet reliability. And with the system like GitProtect, that reliability comes built-in. It’s engineered not just to save data, but to save time.
After all, things move fast. One minute, a repo’s spun up for a quick patch, the next it’s got five contributors and three pipelines hooked into it. In all that motion, expecting someone to remember to hit backup on time (every time) is a gamble. Scheduled automation cuts that risk out. It doesn’t wait on memory, meetings, or who’s on call. It just runs quietly and predictably.
And workflows, where even a slight misstep can cost a release (in a not-so-bad scenario), that kind of reliability isn’t a luxury. It’s how you stay in the game.
[FREE TRIAL] Ensure compliant backup and recovery of critical DevOps data with a 14-day trial 🚀
[CUSTOM DEMO] Let’s talk about how DevOps backup & DR software can help you mitigate the risks






