
Navigating Atlassian’s Data Protection Challenges In The Cloud
With the rise of remote work, Atlassian Product Suite has become much more prevalent among companies for managing their teams and data. Though, not every company dives deep into understanding what cloud security measures Atlassian have and what obligations are rested on the organization’s shoulders.
In this blog post, we are to go through Atlassian’s Data Protection Challenges in the Cloud, but first, let’s figure out what Atlassian’s Cloud Shared Responsibility Model is before we jump into Atlassian Data Protection Gaps.
What helps you understand your duty and obligation, and what responsibilities are on your cloud service providers? The Shared Responsibility model is an answer to this question.
On the main page of Atlassian Cloud Security Shared Responsibility, the cloud service provider emphasizes that together with customers they “are on the same team and are here to support your (customers’) needs across our platform.” Yet, let’s take a closer look at each party’s obligations.
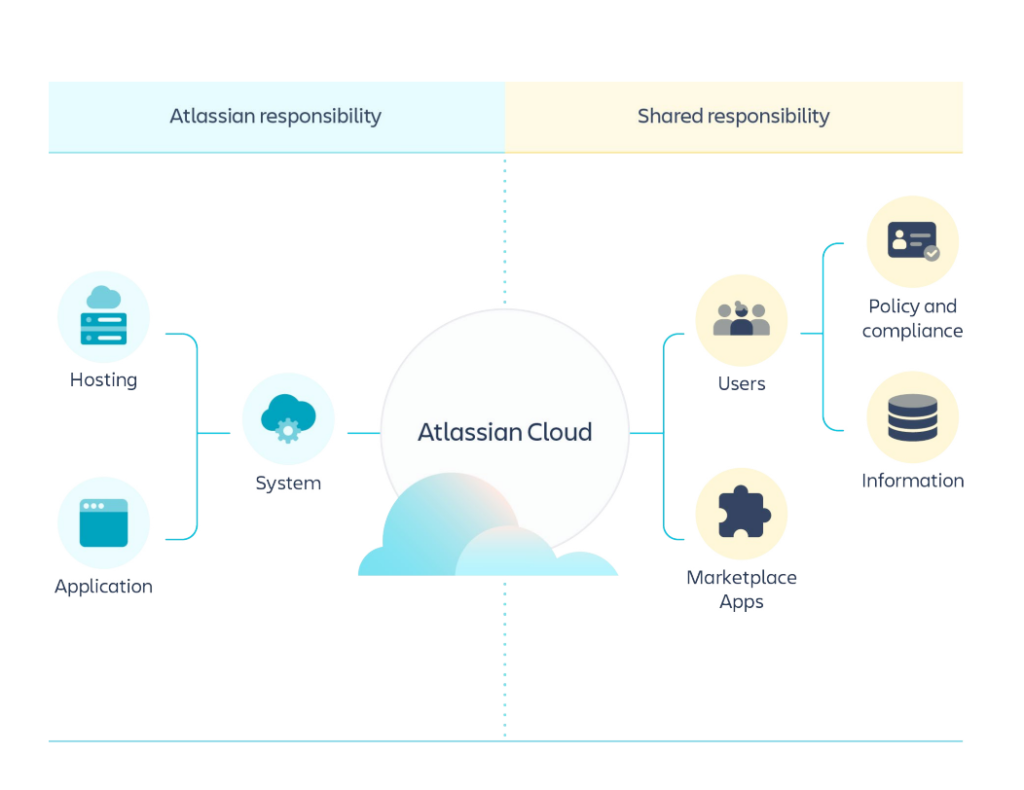
Source: Atlassian Cloud Security Shared Responsibilities
Atlassian Cloud Shared Responsibility model is grounded on four main principles: reliability, security, privacy, and compliance. Though, as you can see from the graphic, Atlassian’s duty is to take care of its system and application running well while a customer is responsible for taking care of its own data, and third-party applications they use. So, if Atlassian experiences an outage or faces any other security risks, Atlassian deals with it, if you experience a ransomware attack, outage, or any other event of failure leading to data loss, it is your responsibility to take care of the problem.

Suppose you want to boost your knowledge about Atlassian Shared Responsibility Model or just brush it up a little bit, you can read our detailed blog post, where we have covered all the key elements you should know about what the Atlassian Cloud Security Shared Responsibility Model is.
Atlassian Data Protection Gaps: the key analysis
Atlassian has backups of its entire service and makes snapshots retained for 30 days (but to support only their infrastructure to work smoothly!). Customers, in their turn, should think about backup of their account data by themselves, as Atlassian has limited recovery capabilities: you can restore your data only within 60 days after you delete it. Here is what Atlassian states in its Security Practices:
“We do not use these backups to revert customer-initiated destructive changes, such as fields overwritten using scripts, or deleted issues, projects, or sites. To avoid data loss, we recommend making regular backups.”
So, as we can see, even Atlassian suggests its customers back up their critical data on a regular basis. It’s important as Atlassian, like other cloud service providers, has its data protection gaps that refer to potential security risks and vulnerabilities in protecting data, and following privacy policies of all Atlassian cloud products (You can find out more about vulnerabilities that Atlassian faced in 2022 in our blog post – 2022 in a nutshell: Atlassian outages and vulnerabilities).
These gaps may appear because of a number of factors. To get a better understanding of the mentioned gaps, let’s dive into them one by one.
Improper data access controls
Sometimes it happens your team configures the access controls incorrectly. It can happen due to different factors: inattentiveness, or misunderstanding of the importance. Anyway, it could lead to the possibility of unauthorized users accessing your company’s sensitive data.
Insufficient logging and monitoring
If you don’t have reliable procedures to capture and monitor logs properly, your organization may experience difficulties to identify and respond to potential cloud security threats. For example, if an attacker gains access to a system and manages to make changes to files of configuration settings, having insufficient logging and monitoring may not capture the event. Thus, it will be even more difficult to identify the source of the attack and determine the extent of the damage.
Accidental deletion of your critical data
We have already mentioned that Atlassian keeps your deleted data only for 60 days. But what if somebody from your team has accidentally deleted critical information and nobody has noticed it on time (as they were working on some other project, for example)? In this case, your data may go forever without any possibility to restore it.
Data changes performed in bulk are to be reverted back
If some bulk changes are made to your Atlassian data that should not have been made, it can lead to inaccurate or incomplete data, which, in its turn, can cause problems down the line and impact your company’s business operations. Why? Because reverting bulk changes can be a time-consuming and resource-intensive process, especially if those changes have been made to a large dataset. Moreover, it can be difficult to revert bulk changes if the organization doesn’t have proper backup or version control in place.
To avoid such problems caused by bulk changes that need to be reverted back, it’s important for your organization to have proper data management, version control procedures, backup, and track of changes to ensure that all of them are properly documented and reviewed before being made.
You can read more about the ways to revert a file to the previous commit in our blog post.
Outdated security protocols
Actually, it is one of the main cloud security tips to update the products you use regularly. Atlassian constantly improves its products and releases security patches and protocols to help its customers mitigate security vulnerabilities to known security threats.
Read about other cloud security tips in our blog post – Atlassian Security Best Practices.
Every company keeps its data for some time which is called the company’s retention policy. It can be due to its organizational, security, and compliance requirements, or due to the need of passing security audits, like ISO 27001 or SOC 2.
On our blog posts about ISO 27001 and SOC 2, you can learn more about those audits and our way to pass those certifications.
Inadequate backup and recovery procedures
If backups are not taken regularly or if they aren’t stored securely, it could result in data loss when an event of a disaster or security breach occurs. For example, to be sure that your Jira, Bitbucket, or Confluence data is safe and sound, your backup should include the following features:
- long-term or infinite retention, which permits meeting legal, security, and compliance requirements and recovering data from any point in time,
- in-flight and at-rest encryption with your own encryption key,
- ransomware protection technology that includes at-rest and in-flight encryption with your own encryption key, immutable storage, etc.,
- Restore and Disaster Recovery Technology, that permits you to restore your Bitbucket, Jira, and Confluence data fast eliminating downtime,
- fulfillment of the 3-2-1 backup rule, under which you have at least 3 copies in at least 2 storage instances, one of which is offsite,
- Monitoring center with email and Slack notifications, advanced audit logs, and tasks to simplify your tracking backup performance.
You can find out more about backup practices that enhance your Atlassian cloud security in our in-depth best practices blog posts: Jira Backup Best Practices and Bitbucket Backup Best Practices.
Are you switching to a DevSecOps operation model? Remember to secure your code with the first professional GitHub, Bitbucket, GitLab, and Jira backup.
The final thought about challenges in the Cloud: data migration
According to the Atlassian announcement, the company is going to support its Server solutions only up to February 2024 (which is less than a year!). That is why all users need to basically, migrate to the cloud.
Still not convinced? Learn more: Jira Migration Pros & Cons and Security Measures.
The process of migration requires a lot of attention from your team. Regardless of whether you plan the migration yourself or use the cloud migration services of specialized Atlassian Partners, you need to have a guarantee that your data is protected on each step. And here comes DevOps backup. It stores the copy of your data on an independent storage and allows you to immediately restore the data to its original state in case something goes wrong during the migration.
But backup can be used as a migration tool itself. Let’s take a look at such use case. GitProtect allows you to make a full copy of your Bitbucket DC data and then restore it directly to the Bitbucket Cloud account. Really, it’s that simple. What’s more, if during the recovery process, you encounter any difficulties and set something wrong, you have permanent access to your data on the storage. So you can even take a few tries – with a guarantee of consistency, availability, and portability of your data.It’s a necessary but challenging task to implement the Atlassian data protection plan. Due to the limited native options provided by Atlassian, you will either need to create your own backup script, perform it and monitor its performance which can be time- and resource-consuming in a long-term perspective, or use a third-party tool, like GitProtect.io, a turn-key solution for DevOps automated backups, to keep your data accessible and recoverable, guaranteeing your business continuity and smooth cloud migration.






