
Cyber Insurance: Why Backup Is Key To Lower Premiums & Higher Eligibility
As the rate of ransomware attacks keeps growing, the demand for cyber insurance is also greater. The State of Ransomware 2025 report by Sophos outlines that nearly 50% of companies in the report paid ransom. This underscores the need for stronger security measures — not only for data protection but also for cyber insurance eligibility. Since risk reduction improves eligibility, here are five key requirements for cyber insurance eligibility:
- Multifactor authentication (MFA)
- Cybersecurity training
- Strong backup & disaster recovery
- Identity access management (IAM)
- Data classification
From the insurer’s perspective, the equation is straightforward:
No proactive cyber defenses = greater risk of data loss.
Greater risk of data loss = greater likelihood of an insurance payout.
So, if there is no action to protect data and cloud services from the organization’s side, the insurance company will limit or even deny coverage. It’s important to remember that cyber insurance is financial recovery and not data recovery. A tested incident response plan, along with cyber threat protection and data backup, supports business continuity and helps secure sensitive data.
Cyber insurance and data loss
New sophisticated cyber threats emerge every day, so the importance of cyber insurance keeps growing, too. While not every attack can be prevented, organizations should proactively leverage security measures such as multi-factor authentication, backup, and disaster recovery. Such data protection strategies are a huge part of any reliable risk management plan. This means stronger data security and better cyber insurance eligibility. Reliable cybersecurity measures decrease the risk of data loss, while cyber insurance supports the financial side of dealing with cyber threats.
Top 3 risks in DevOps:
- Ransomware – 2024 shows an 11% increase compared to 2023. Take a look for yourself, quarter by quarter:
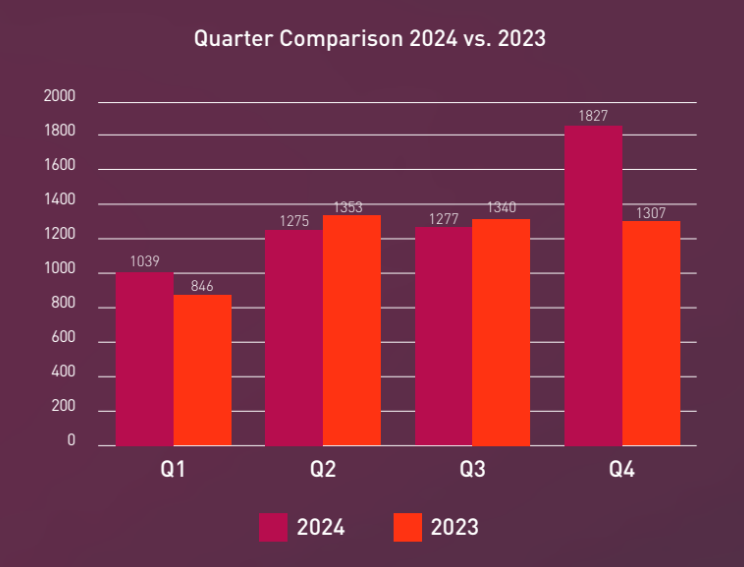
Source: Hacker News
- Human errors, such as accidental deletion, remain the main contributor to data breaches in 2024, with 95%.
- Without secure backups, DR outages can leave organizations without access to their data, resulting in a stop of business operations, damaged reputation, and violated compliance regulations.
Implementing cyber insurance used to be simple; however, given the current threat landscape, companies must demonstrate a range of strong cybersecurity measures to get approved for coverage. In order to qualify for an insurance policy, you shall introduce the controls that the insurer requires.
Compliance in the context of cyber insurance
Insurers, similarly to regulations, demand evidence of concrete safeguards like MFA, IAM, security training, and reliable data backups with flexible recovery. Coalition (a major cyber insurer) has stated the following in regards to the requirement of secure backups:
Maintain good data backups
A good data backup can mean the difference between a complete loss or a full recovery after a cyber attack. Maintaining data backups may also be a recommendation for your cyber insurance policy, depending on your organization’s data.
Redundancy is critical in a good backup strategy. Businesses should use both on- and off-site backups for storing essential data. It’s critical that at least one form of backup be stored completely separate from the primary network, such as in an external drive or tape. Store one copy on an off-site device, like a cloud server.
Test your backups by frequently conducting a full recovery. All too often, organizations only test their backups when they need them, and find out that their restoration has failed or backups were inadequate. In the case of increasingly common ransomware attacks, backups are the key determinant of whether a ransom payment is made or not. Without backups, a business is at the mercy of threat actors
At the same time, regulated organizations are still legally required to implement secure backups and DR. This includes NIS2 and Article 21, which mandates:
protect network and information systems and the physical environment of those systems from incidents, and (…) include at least the following: (…) business continuity, such as backup management and disaster recovery, and crisis management
DORA (Digital Operational Resilience Act) in Article 11 states that:
financial entities, other than microenterprises, shall include in the testing plans scenarios of cyber-attacks and switchovers between the primary ICT infrastructure and the redundant capacity, backups, and redundant facilities necessary to meet the obligations set out in Article 12
Then, Article 12 outlines the required backup policies, procedures, restore, and recovery processes along with correct methods. Shortly put, financial entities must implement redundant data backup, which aligns with what insurers expect for cyber insurance eligibility.
The importance of backup & data recovery in cyber insurance eligibility
Since regulations demand immutable backups and disaster recovery, insurers see them as a baseline for eligibility. Even outside of highly regulated sectors, data theft is common, so controls like MFA and immutable cloud backups are necessary to qualify and avoid restrictions. Now, verified compliance with the set out backup and DR obligations ensures data integrity, fewer irreversible losses, shorter to no outages, and significantly reduces payout probability. This makes backup and disaster recovery a crucial aspect of cyber insurance.
Why RTO & RPO metrics matter
Every reliable incident response plan relies on regular backups, recovery solutions, proper risk assessment, and an organized incident response team. Recovery Time Objective (RTO), establishes acceptable downtime, while Recovery Point Objective (RPO) measures acceptable data loss. Shorter RTO and RPO show insurers that a company can restore operations quickly with minimal data loss. This is especially true for highly regulated industries such as healthcare, government, and financial services. As stated by Cyber Insurance Academy, when it comes to RTO and RPO, cyber insurance professionals are advised to verify if the following have been considered by the insured:
- ‘Has the amount of data that the client can afford to lose been balanced against the impact it would have on their business? (…)
- Has the client considered the cost of more frequent backups versus the risk of having to redo work if data is lost?
- Have options for spacing backups and achieving longer-term data retention been explored by the client?’
Carefully optimized RTO and RPO metrics supported by reliable data backup and an incident response plan mean greater eligibility for cyber insurance and better terms for policies. Make sure to minimize downtime and to avoid potential future incidents, always carry out a post-incident review.
Most SaaS providers operate under the Shared Responsibility Model, which essentially establishes that the user is responsible for their data, while the providers’ duty is the underlying infrastructure. For instance, take a look at GitHub’s terms of service in terms of account security:
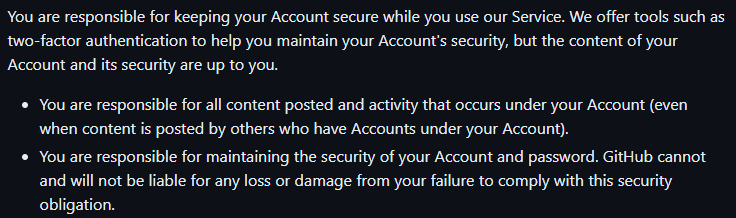
Source: GitHub Terms of Service
Insurers recognize this division of responsibility, so they will check if the Shared Responsibility Model is addressed. Make sure to implement strong data security measures and consider the potential risks. It is your duty to protect your confidential data, deal with compromised user accounts, detect any unusual behavior, and prevent potentially infected systems from doing any further damage. Now, third-party backup and recovery strategies fall under your duties within this model. GitLab refers to data backup and recovery in its documentation and states the following:

Source: GitLab Docs
For an in-depth guide on how to back up your GitLab data securely, check out The Ultimate Guide to GitLab Backup.
Service providers advise their users to implement third-party backup and disaster recovery strategies, and again, insurers are aware of this, so it is essential to implement cybersecurity measures addressing the Shared Responsibility Model.
👉 Looking for cloud backup solutions? Be sure to visit: 11 SaaS Backup Solutions And Tools To Keep Your Data Safe
Backup and recovery features insurers look for
To address the risks and the increasing requirements of DevSecOps, insurers demand a reliable backup and incident response plan. Data backup and recovery serve as the last line of defense against data loss, corruption, and cyber threats. In terms of third-party backup & DR, organizations must demonstrate effectiveness and be audit-ready. A strong data backup strategy minimizes downtime, protecting against financial loss and maintaining customer trust.
The key security features and functionalities of comprehensive solutions like GitProtect.io, that ensure compliance and cyber insurance eligibility, include:
- AES encryption (in-transit and at-rest)
- Ransomware protection
- 3-2-1 backup rule
- Replication
- Backup scheduler within your organization’s requirements
- Automated data backups
- Unlimited retention
- Immutable, WORM-compliant storage
- Full data recovery, granular restore, point-in-time restore, cross-over recovery
- Compliance with industry standards
- Monitoring, notifications, audits
- A unified platform with an intuitive and simple interface
- Every-scenario-ready Disaster Recovery solutions
By guaranteeing your sensitive data is backed up and implementing data retention policies, you can swiftly recover from any cybersecurity incident and get back to your primary objectives. Even in the face of accidental deletions, service outages, or ransomware attacks, you should be able to access and restore your data in accordance with your incident response plan and the RTO & RPO metrics. Providers should store backups in secure locations to avoid revealing sensitive information. This proves to the insurer that your data is secure, operations are compliant, and your company can be considered as low-risk.
Looking to improve your cyber security eligibility with strong backup and recovery?
→ [READ MORE] DevOps Backup Best Practices To Keep Your Data 100% Safe 🎓
→ [FREE TRIAL] Take A Leading DevOps Backup Tool For A Spin – Free 14-day trial 🚀






